Meteorological environment monitoring equipment supplier
Insist on doing high-precision customer favorite technology products
Campus Weather Station Construction Plan for Science Education aims to provide students with immersive learning experiences through on-site observation and data collection. This program integrates real-time weather data, allowing students to participate in observation and analysis, incorporating meteorological science into school life, popularizing general knowledge, and strengthening environmental awareness. Based on practical construction and operation, it promotes scientific literacy and creates an interactive educational environment.
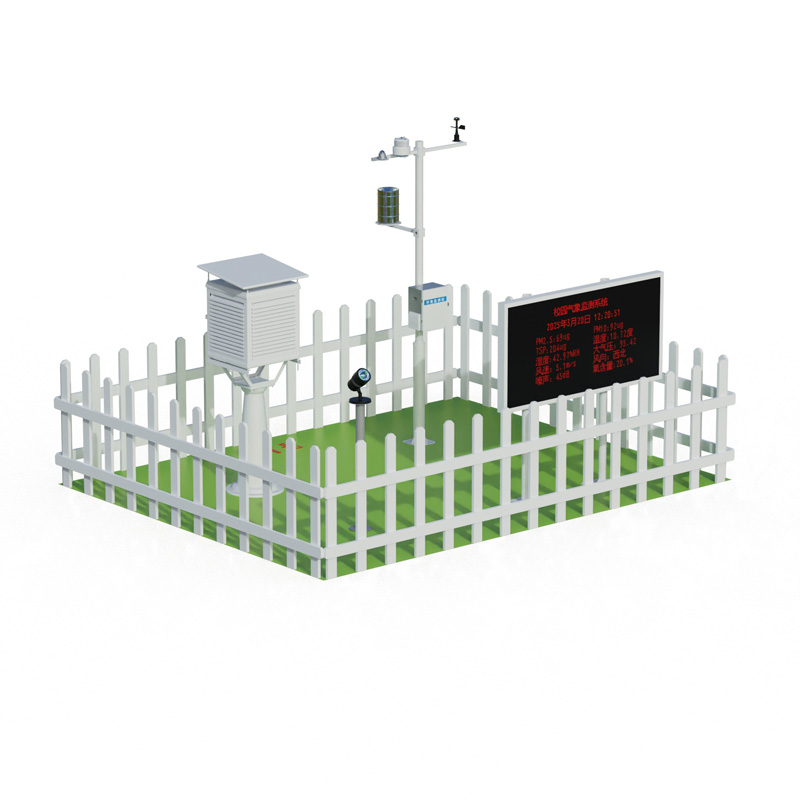
Campus Weather Station Construction Plan for Science Education is an important component of current educational innovation. Through systematic design, it creates a realistic meteorological learning environment for students. The core of this program lies in combining theoretical knowledge with practical operation, transforming students from passive recipients to active explorers. The construction of the immersive learning scenario relies on the hardware facilities and software support of the weather station. The station is usually equipped with temperature sensors, hygrometers, anemometers, rain gauges, and other equipment, capable of collecting real-time weather data. Students can access this information through displays or mobile devices to observe the changes in weather phenomena.
The presentation of real-time weather data and phenomena is a key aspect of the program. The high frequency of data updates reflects the local microclimate characteristics. Students can record temperature fluctuations, precipitation patterns, or wind speed changes to understand the basic principles of meteorology. This real-time aspect not only enhances the timeliness of learning but also stimulates students' curiosity about natural phenomena. Through long-term observation, they can identify meteorological patterns in seasonal changes and apply classroom knowledge to real-world scenarios.
On-site observation, data collection, and analysis constitute the core activities for student participation. Under the guidance of teachers, students work in groups to operate instruments and conduct regular measurements. They learn to calibrate equipment, record readings, and use simple statistical tools to analyze data trends. For example, by comparing temperature data from different dates, students can discuss the impact of climate change. This hands-on process cultivates scientific method skills, such as hypothesis testing and error analysis. After data collection, students can create charts or reports and share their findings in the classroom or on campus, promoting collaborative learning.
Integrating meteorological science into school life is an extended goal of this program. Weather station data can be integrated into school broadcasts, websites, or bulletin boards, becoming part of daily information. The school can organize weather-themed activities, such as "Meteorology Day" exhibitions or environmental lectures, inviting students to showcase their observation results. Furthermore, meteorological knowledge can be integrated across disciplines, such as discussing climate zones in geography class or studying the impact of weather on ecosystems in biology class. This integration makes science popularization more engaging and enhances the scientific atmosphere within the school culture.
It allows students to participate in real-world observations, directly disseminating meteorological knowledge and strengthening environmental awareness. Through firsthand experience, students understand the connection between weather and human activities. For example, when observing changes in air quality, they can discuss the impact of pollution sources; when recording extreme weather events, they can learn about disaster prevention. This experiential education deepens their understanding of environmental protection and encourages them to take actions to conserve resources and reduce their carbon footprint. The program also encourages students to propose improvement suggestions, such as optimizing campus greenery to regulate the microclimate, thus transforming learning into practical initiatives.
In short, Campus Weather Station Construction Plan for Science Education not only provides a technological platform but also shapes an interactive learning ecosystem. Based on empirical methods, it allows students to accumulate experience through observation and improve their scientific literacy. The implementation of the program requires consideration of equipment maintenance, teacher training, and curriculum integration to ensure long-term effectiveness. Through this practical approach, schools can cultivate a new generation with a stronger sense of environmental responsibility, laying the foundation for sustainable development education.