Meteorological environment monitoring equipment supplier
Insist on doing high-precision customer favorite technology products
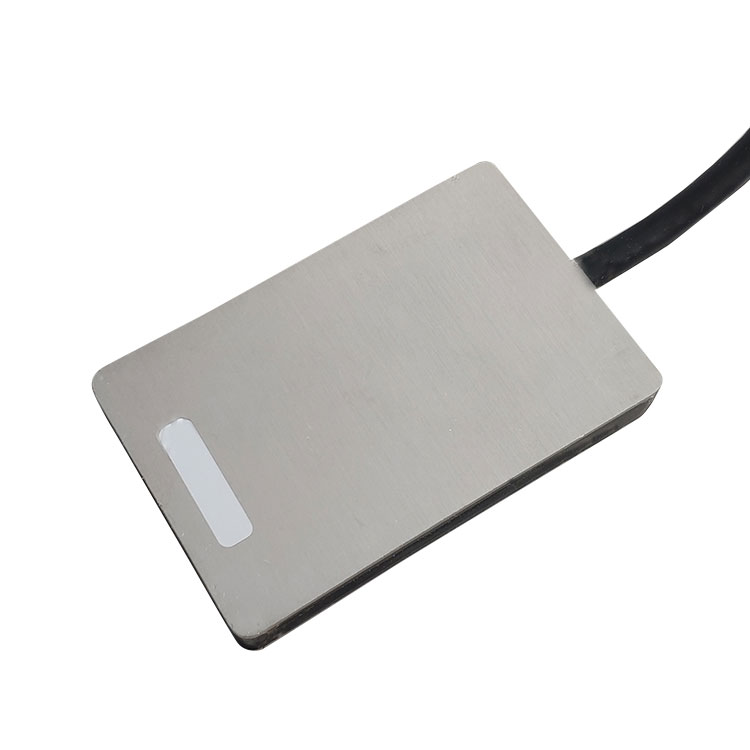

1. Soil heat flux sensor product overview
Soil heat flux sensor uses thermopile to measure soil heat flux, which is mainly used to measure soil energy balance and soil layer thermal conductivity.Soil heat flux sensor, also known as heat flow plate, soil heat flux plate, heat flow meter and other names, is an instrument used to measure heat flux and can be used for internal measurements of soil.It outputs in the form of voltage through a thermopile, and the voltage is proportional to the heat flux.It is easy to operate and is especially suitable for measuring the thermal conductivity of soil, building walls, and glass walls.The soil heat flux value is measured using a heat flux plate buried 2cm in the soil.Throughout the year, it changes with the seasons.In summer, the soil heat flux is positive, and heat enters the soil layer, and the amount is larger; in winter, the soil heat flux is negative, and the amount of heat in the soil is negative.Heat is released to the atmosphere, but in a smaller amount.
2.Application scope of Soil heat flux sensor
This product can be widely used in environment, agriculture, forestry, planting, construction, and other fields.
3.Soil heat flux sensor technical parameters
Power supply voltage: □12-24V□5V
Output signal: □Current type 4~20mA□0-2V□RS485 customized
Measuring range: -200 to 200 w/m2
Internal resistance is less than 300Ω
Measurement accuracy: less than 5%
Heat flow calculation formula
Heat flow (w/m2) = coefficient (w*m-2/mv)*output (mv)
Working current: About 26mA when powered on by 12V
4.Soil heat flux sensor functional characteristics
1.Small size, fast and accurate measurement
2.Low power consumption design, adopting reasonable power consumption control mode
3.Stable performance
5.Soil heat flux sensor measurement method
1.Measurement method in soil
The board surface should be perpendicular to the direction of heat flow and placed horizontally in the soil layer.The burial depth of the sensor is usually 3-10 cm from the natural underlying surface.Try to avoid setting it directly on the soil surface, because the natural underlying surface is not a geometric plane, and slight fluctuations on the surface will make the sensor readings lose their representativeness.At the same time, the upper surface of the sensor may also produce radiation errors if it is in direct contact with the air.Usually, a representative area is selected at the observation site, and a profile is dug vertically downward with a shovel.
Measure the required depth from the soil surface downward along the profile, and then hollow it out in the horizontal direction.The size is just right for placing the heat flow plate, so that the upper and lower sides of the sensor can maintain good contact with the soil.Lead the wires along the profile and then Soil backfill.But it should be noted that the buried depth of the heat flow plate should be the distance between its center line and the soil surface.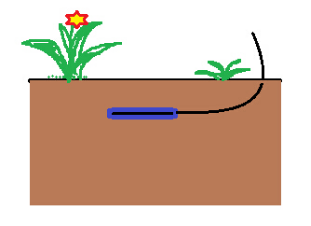
2.Measurement method on wall
First, apply Vaseline evenly on the surface of the heat flow sensor, and stick the heat flow sensor coated with Vaseline on the wall surface so that the wall and the heat flow sensor can be in close contact.After staying there for a few minutes, the measurement can be started after the heat flow sensor adapts to the ambient temperature.